Election
U.S. presidential elections can be tough on the nerves, and 2020 promises to be no different. Politics can bring out strong emotions and biases, but investors would be wise to put these aside when making investment decisions.
Benjamin Graham, the father of value investing, famously noted that “In the short run, the market is a voting machine but in the long run, it is a weighing machine.” He wasn’t literally referring to the intersection of elections and investing, but he could have been. Markets can be especially choppy during election years, with sentiment often changing as quickly as candidates open their mouths.
Graham first made his analogy in 1934, in his seminal book, “Security Analysis.” Since then there have been 22 U.S. election cycles, and we’ve analyzed them all to help you and your clients prepare for investing in these potentially volatile periods. Below we highlight three common mistakes made by investors during U.S. election years and offer ways to avoid these pitfalls and invest with confidence in 2020.
Mistake #1: Investors worry too much about which party wins the election
There’s nothing wrong with wanting your candidate to win, but investors can run into trouble when they place too much importance on election results. That’s because U.S. elections have, historically speaking, made essentially no difference when it comes to long-term investment returns.
“Presidents get far too much credit, and far too much blame, for the health of the U.S. economy and the state of the financial markets,” says Capital Group economist Darrell Spence. “There are many other variables that determine economic growth and market returns and, frankly, presidents have very little influence over them.”
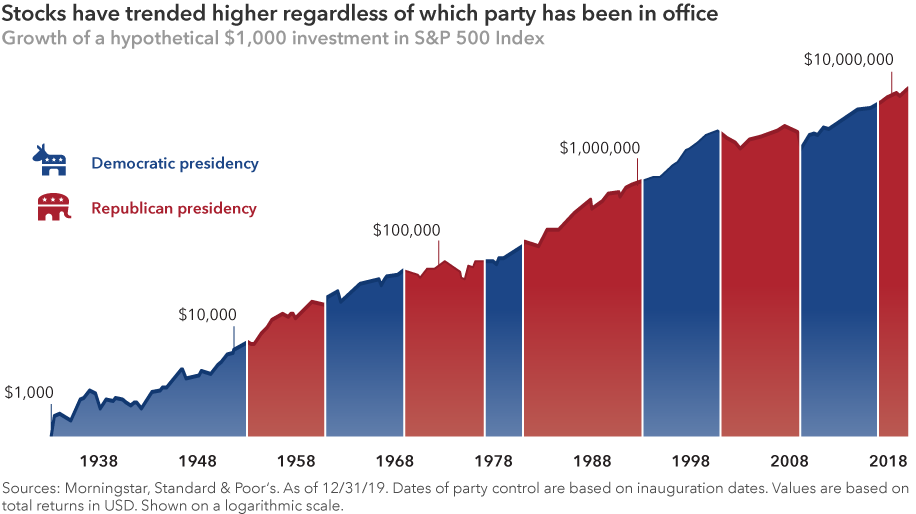
What should matter more to investors is staying invested. Although past results are not predictive of future returns, a US$1,000 investment in the S&P 500 made when Franklin D. Roosevelt took office would have been worth over US$14 million today. During this time there have been exactly seven Democratic and seven Republican presidents. Getting out of the market to avoid a certain party or candidate in office could have severely detracted from an investor’s long-term returns.
By design, elections have clear winners and losers. But the real winners were investors who avoided the temptation to base their decisions around election results and stayed invested for the long haul.
Mistake #2: Investors get spooked by primary season volatility
Markets hate uncertainty, and what’s more uncertain than the U.S. election primary season (i.e. a series of state elections to determine each party’s nominee)? With so many candidates on the campaign trail — 11 Democrats were still running when primaries kicked off in early February — the range of outcomes can feel daunting.
But volatility caused by this uncertainty is often short-lived. After the primaries are over and each party has selected its candidate, markets have tended to return to their normal upward trajectory.
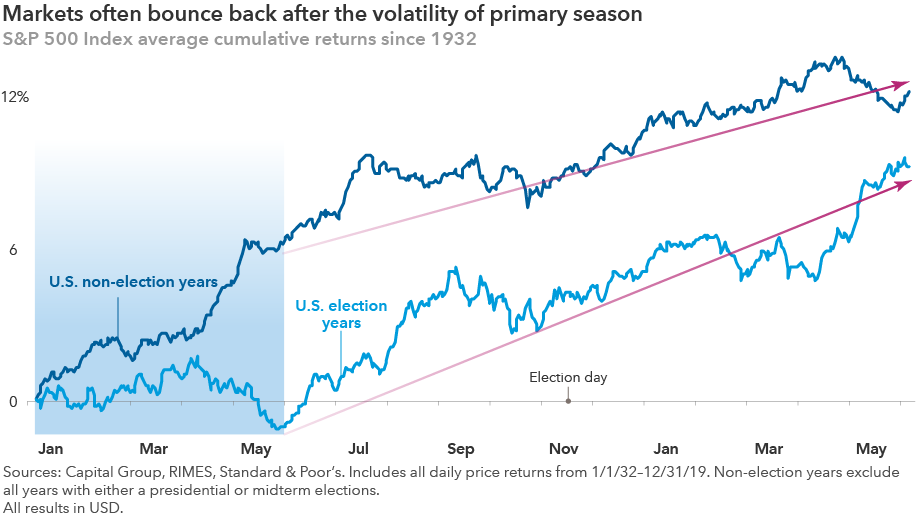
Election year volatility can also bring select buying opportunities. U.S. policy proposals during primaries often target specific industries, putting pressure on share prices. This cycle, it’s the health care sector that’s in the spotlight as several candidates have proposed overhauls to drug pricing and the health care system.
Does that mean you should avoid this sector altogether? Not according to Rob Lovelace, an equity portfolio manager with 34 years of experience investing through many election cycles. “When everyone is worried that a new government policy is going to come along and destroy a sector, that concern is usually overblown,” Lovelace says. “Companies with good drugs that are really helping people will be able to get into the market, and they will get paid for it.”
In the past, those targeted sectors have often rallied after the campaign spotlight dimmed. It happened with health care following the 2016 presidential and 2018 midterm elections in the U.S., and has happened with other sectors in the past. This can create buying opportunities for investors with a contrarian point of view and the ability to withstand short-term volatility.
Mistake #3: Investors try to time the markets around politics
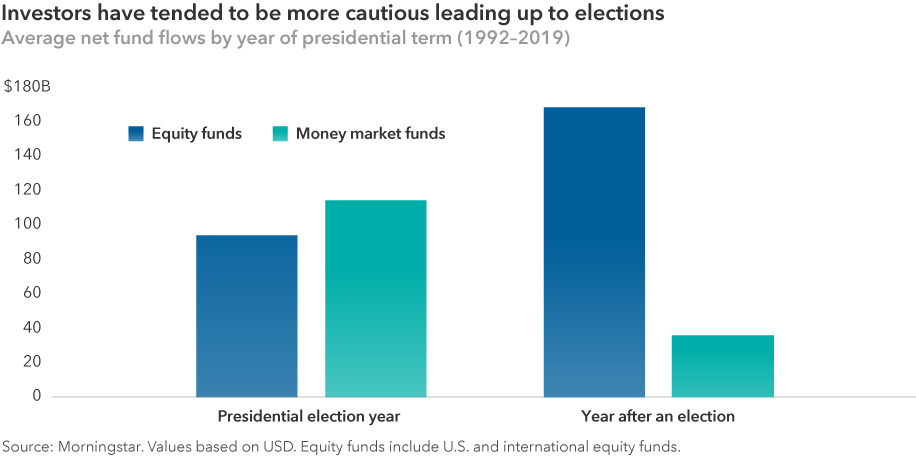
If you’re nervous about the markets in 2020, you’re not alone. U.S. presidential candidates often draw attention to the country’s problems, and campaigns regularly amplify negative messages. So maybe it should be no surprise that investors have tended to be more conservative with their portfolios ahead of presidential elections.
Since 1992, investors have poured assets into U.S. money market funds — traditionally one of the lowest risk investment vehicles — much more often leading up to elections. By contrast, equity funds have seen the highest net inflows in the year immediately after a U.S. presidential election. This suggests that investors may prefer to minimize risk during election years and wait until after uncertainty has subsided to revisit riskier assets like stocks.
But timing the market is rarely a winning long-term investment strategy, and it can pose a major problem for portfolio returns. To verify this, we analyzed investment returns over the last 22 U.S. election cycles to compare three hypothetical investment approaches: being fully invested in equities, making monthly contributions to equities, or staying in cash until after the election. We then calculated the portfolio returns after each cycle, assuming a four-year holding period.
The hypothetical investor who stayed in cash until after the election had the worst outcome of the three portfolios in 16 of 22 periods. Meanwhile, investors who were fully invested or made monthly contributions during election years came out on top. These investors had higher average portfolio balances over the full period and more often outpaced the investor who stayed on the sidelines longer. (For more information on the methodology of this analysis, please refer to the notes section at the end of this article or the full Guide to investing in a U.S. election year.)
Sticking with a sound long-term investment plan based on individual investment objectives is usually the best course of action. Whether that strategy is to be fully invested throughout the year or to consistently invest at regular intervals, the bottom line is that investors should avoid timing the market around politics. As is often the case with investing, the key is to put aside short-term noise and focus on long-term goals.
How can investors avoid these mistakes?
- Don’t allow election predictions and outcomes to influence investment decisions. History shows that U.S. election results have very little impact on long-term returns.
- Expect volatility, especially during U.S. election primary season, but don’t fear it. View it as a potential opportunity.
- Stick to a long-term investment strategy instead of trying to time markets around elections. Investors who were fully invested or made regular, monthly investments did better than those who stayed in cash in election years.
Download the Guide to investing in a U.S. election year (PDF)
Our latest insights
-
-
Global Equities
-
Artificial Intelligence
-
Technology & Innovation
-
RELATED INSIGHTS
-
-
Artificial Intelligence
-
Technology & Innovation
Commissions, trailing commissions, management fees and expenses all may be associated with mutual fund investments. Please read the prospectus before investing. Mutual funds are not guaranteed, their values change frequently and past performance may not be repeated.
Unless otherwise indicated, the investment professionals featured do not manage Capital Group‘s Canadian mutual funds.
References to particular companies or securities, if any, are included for informational or illustrative purposes only and should not be considered as an endorsement by Capital Group. Views expressed regarding a particular company, security, industry or market sector should not be considered an indication of trading intent of any investment funds or current holdings of any investment funds. These views should not be considered as investment advice nor should they be considered a recommendation to buy or sell.
Statements attributed to an individual represent the opinions of that individual as of the date published and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of Capital Group or its affiliates. This information is intended to highlight issues and not be comprehensive or to provide advice. For informational purposes only; not intended to provide tax, legal or financial advice. We assume no liability for any inaccurate, delayed or incomplete information, nor for any actions taken in reliance thereon. The information contained herein has been supplied without verification by us and may be subject to change. Capital Group funds are available in Canada through registered dealers. For more information, please consult your financial and tax advisors for your individual situation.
Forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance, and actual events and results could differ materially from those expressed or implied in any forward-looking statements made herein. We encourage you to consider these and other factors carefully before making any investment decisions and we urge you to avoid placing undue reliance on forward-looking statements.
The S&P 500 Composite Index (“Index”) is a product of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC and/or its affiliates and has been licensed for use by Capital Group. Copyright © 2024 S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, a division of S&P Global, and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Redistribution or reproduction in whole or in part are prohibited without written permission of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC.
FTSE source: London Stock Exchange Group plc and its group undertakings (collectively, the "LSE Group"). © LSE Group 2024. FTSE Russell is a trading name of certain of the LSE Group companies. "FTSE®" is a trade mark of the relevant LSE Group companies and is used by any other LSE Group company under licence. All rights in the FTSE Russell indices or data vest in the relevant LSE Group company which owns the index or the data. Neither LSE Group nor its licensors accept any liability for any errors or omissions in the indices or data and no party may rely on any indices or data contained in this communication. No further distribution of data from the LSE Group is permitted without the relevant LSE Group company's express written consent. The LSE Group does not promote, sponsor or endorse the content of this communication. The index is unmanaged and cannot be invested in directly.
BLOOMBERG® is a trademark and service mark of Bloomberg Finance L.P. and its affiliates (collectively “Bloomberg”). Bloomberg or Bloomberg’s licensors own all proprietary rights in the Bloomberg Indices. Neither Bloomberg nor Bloomberg’s licensors approves or endorses this material, or guarantees the accuracy or completeness of any information herein, or makes any warranty, express or implied, as to the results to be obtained therefrom and, to the maximum extent allowed by law, neither shall have any liability or responsibility for injury or damages arising in connection therewith.
MSCI does not approve, review or produce reports published on this site, makes no express or implied warranties or representations and is not liable whatsoever for any data represented. You may not redistribute MSCI data or use it as a basis for other indices or investment products.
Capital believes the software and information from FactSet to be reliable. However, Capital cannot be responsible for inaccuracies, incomplete information or updating of the information furnished by FactSet. The information provided in this report is meant to give you an approximate account of the fund/manager's characteristics for the specified date. This information is not indicative of future Capital investment decisions and is not used as part of our investment decision-making process.
Indices are unmanaged and cannot be invested in directly. Returns represent past performance, are not a guarantee of future performance, and are not indicative of any specific investment.
All Capital Group trademarks are owned by The Capital Group Companies, Inc. or an affiliated company in Canada, the U.S. and other countries. All other company names mentioned are the property of their respective companies.
Capital Group funds are offered in Canada by Capital International Asset Management (Canada), Inc., part of Capital Group, a global investment management firm originating in Los Angeles, California in 1931. Capital Group manages equity assets through three investment groups. These groups make investment and proxy voting decisions independently. Fixed income investment professionals provide fixed income research and investment management across the Capital organization; however, for securities with equity characteristics, they act solely on behalf of one of the three equity investment groups.
The Capital Group funds offered on this website are available only to Canadian residents.
 Rob Lovelace
Rob Lovelace